Table of Contents
1. What’s Sampling Time All About? 🎯
Sampling Time (ST) is a free open source plugin for QGIS that automates multiple methods for spatial data collection, including judgmental, random, systematic, stratified, and cluster techniques. Generate precise points with customizable outputs to streamline spatial analysis. Its versatility makes it ideal for applications in fields such as environmental studies, urban planning, and resource management. Sampling Time stands out as a reliable solution for users seeking efficiency and accuracy in their geospatial workflows.
The primary goal of Sampling Time is to offer a robust suite of tools for generating sampling points on vector layers. By streamlining the sampling process, the plugin automates workflows and removes complexity, making spatial data collection more efficient and user-friendly. Advanced features, such as customizable parameters and automated labeling, empower users to design precise sampling strategies. Whether working on large-scale projects or focused studies, Sampling Time adapts seamlessly to meet diverse analytical needs.
Sampling Time is designed to make spatial analysis accessible to everyone, regardless of their GIS experience. With its intuitive interface, users can effortlessly create sampling areas, define exclusion zones, generate strata, and build clusters in just a few clicks. The guided, step-by-step process ensures clarity and ease of use, even for beginners. By automating tasks like labeling and symbology customization, the plugin provides a seamless workflow, reaching a broad audience while maintaining professional-grade functionality.
2. The Legal Stuff (Don’t Skip This!) 🔒
Sampling Time Plugin is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
Sampling Time Plugin is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with Sampling Time Plugin. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/

3. About the Creator (Hey There!) 👋

Marcel A. Cedrez , the developer of the Sampling Time plugin for QGIS, is a hydrogeologist with over a decade of experience in environmental studies and a strong passion for geospatial analysis. Leveraging artificial intelligence, he ventured into software development to create accessible tools that simplify complex spatial workflows.
Marcel’s programming journey began with R, where he developed scripts for advanced geostatistical analyses in QGIS. He later expanded his skills by creating public Shiny online apps, such as Histogram and Map Generator and GeoSample Pro Analyzer, aimed at enhancing spatial data visualization and sampling workflows. These experiences laid the groundwork for “Sampling Time”, his first QGIS plugin, designed to automate sampling techniques with precision, adaptability, and user-friendly features.
As an educator with thousands of hours of teaching experience, over 140 video tutorials on GIS and spatial analysis on his YouTube channel, and a variety of specialized courses on topics such as geostatistics, QGIS, and hydrogeology, Marcel is dedicated to empowering users of all levels to achieve their goals with innovative geospatial tools.
4. The AI-Powered Journey: From Concept to Creation 🚀
Sampling Time was born from Marcel A. Cedrez’s expertise in sampling techniques, built through years of field sampling work and designing sampling plans with QGIS and other GIS software. While the creation of the Soil Sampling Techniques Using QGIS course in 2020 laid important groundwork, it was the revolutionary potential of artificial intelligence that transformed this project, taking automation to the next level. By leveraging artificial intelligence technologies, Marcel was able to dramatically expand his capabilities, enabling him to bridge his hydrogeological expertise with advanced software development. The result is more than just a plugin – it’s a testament to how artificial intelligence can empower professionals to transcend their traditional boundaries, turning domain expertise into powerful software solutions. Through artificial intelligence assistance, Marcel was able to multiply his capabilities and create a sophisticated tool that automates complex sampling processes, demonstrating how artificial intelligence can transform subject matter experts into innovative software developers.
Marcel reflects: “With the skills I’ve gained and the leverage of artificial intelligence, I now feel empowered to create applications that enhance GIS workflows and simplify geospatial analysis for a wide range of users”
5. Connect, Cite & Credits 🤝
For questions, feedback, or collaboration opportunities, reach out to Marcel at marcel.a@giscourse.online
How to cite: Cedrez, M. A. (2024). Sampling Time: A QGIS plugin for automating sampling techniques in geospatial analysis (Version 1.0.0). GitHub Plugin Repository: https://github.com/MarcelGeoRGB/Sampling-Time-QGIS-Plugin
This plugin was developed using AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4 (o1, o1-preview, o1-mini) and Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet, combined with years of experience in QGIS.
6. Download and installation 💾
The plugin is officially available in the QGIS plugins repository, which ensures it has passed QGIS’s quality standards and security reviews. This official approval means users can trust the plugin’s reliability and compatibility with their QGIS installation. Additionally, being in the official repository enables automatic updates and notifications when new versions are available.
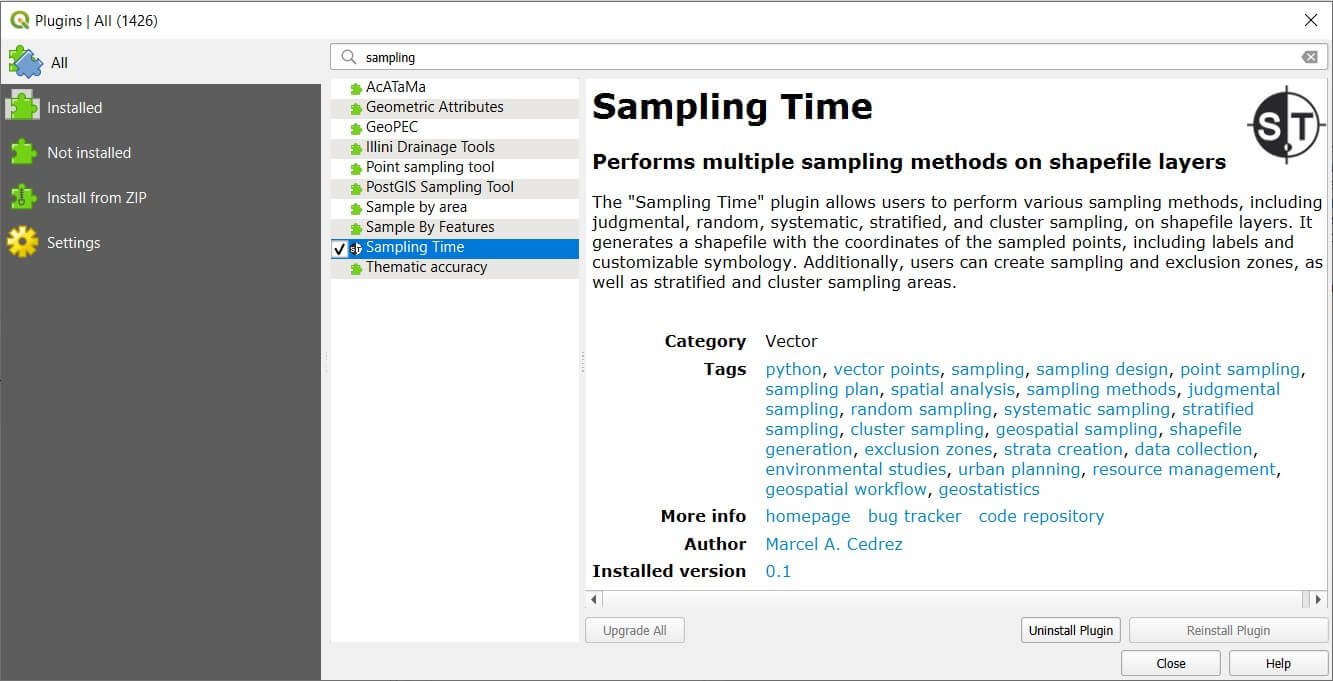
It can be easily downloaded and installed directly from QGIS. Open QGIS and navigate to Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins from the main menu. In the pop-up window, select All, search for Sampling Time, check the box, and click Install Plugin. Once installed, the Sampling Time plugin will be available under the Vector tab in the main menu toolbar. Restarting QGIS may be required to complete the installation process.
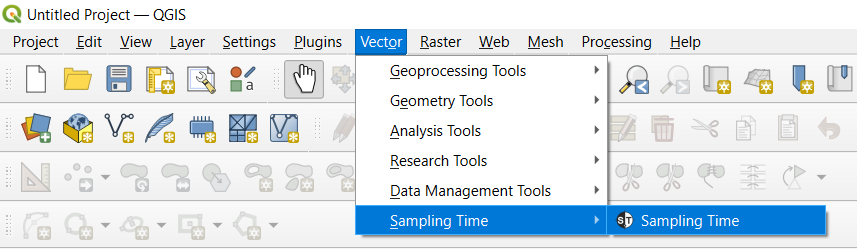
For manual installation, you can download the ZIP file either from our QGIS plugins repository using the blue Download button, or from our GitHub repository by clicking the green Code button and selecting Download ZIP. To install it manually, open QGIS, go to Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins in the main menu, and select Install from a ZIP. Locate the downloaded ZIP file, upload it, and click Install Plugin.
Note: Restarting QGIS may be required to complete the installation process, regardless of the installation method chosen.
7. Plugin Interface ⚙️
The interface of Sampling Time is divided into three panels: the Initiation Panel, the Reset/Close Panel, and the Sampling Methods Panel.
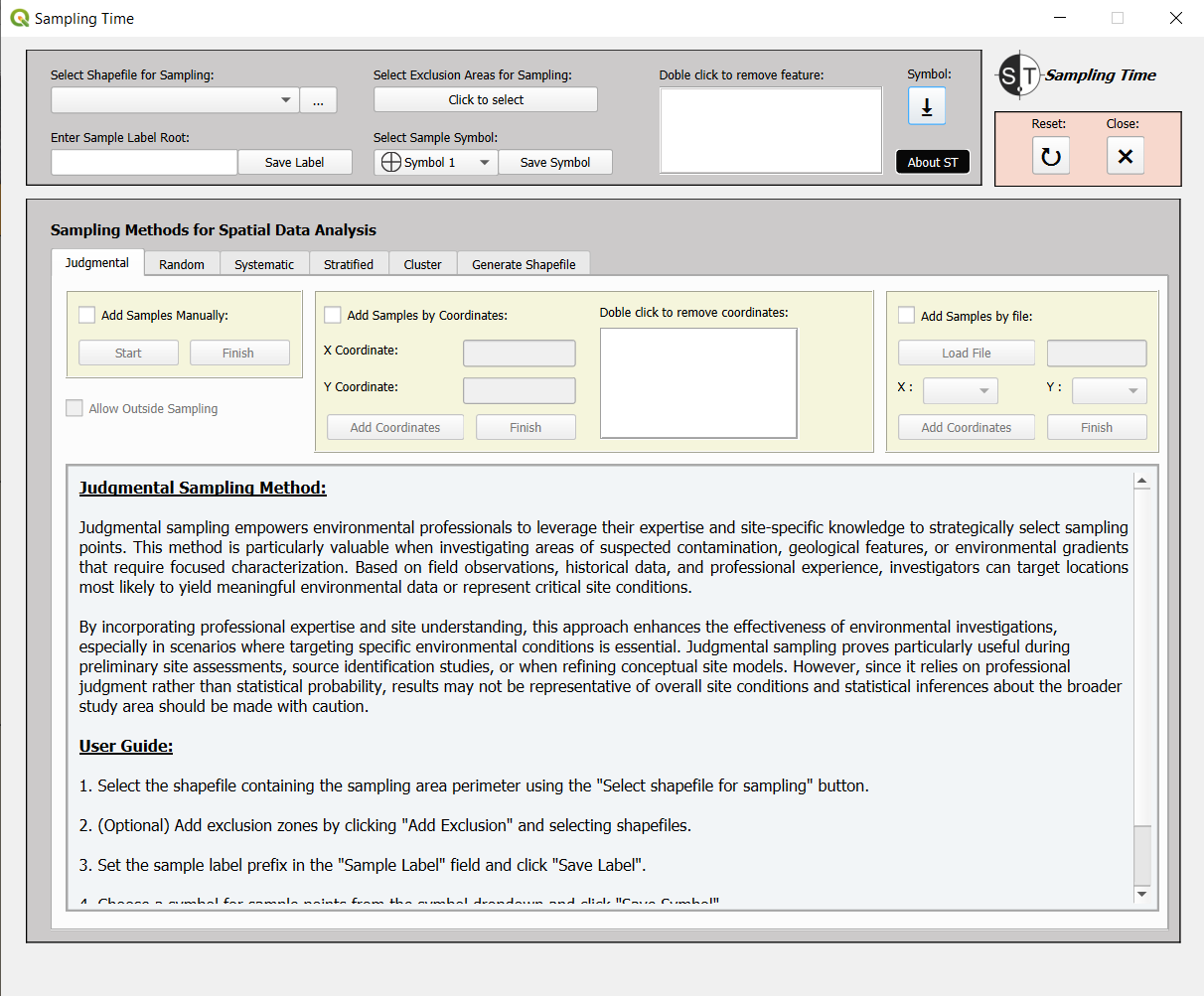
7.1. Initiation Panel
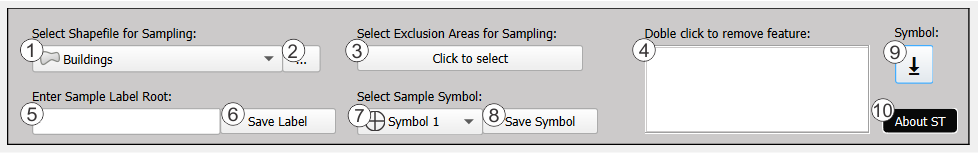
7.1.1 Shapefiles for Sampling Area
To perform any type of sampling, a shapefile containing the sampling area must be loaded. This shapefile may consist of a single feature (suitable for judgmental, random, or systematic sampling) or multiple features (used for cluster or stratified sampling). If the sampling area is already available in the QGIS Layers panel, Button 1 can be used to select it from the dropdown menu. In cases where the desired layer does not appear, the Reset Button (Reset/Close Panel, section 7.2) should be pressed to refresh the plugin and update the list of available layers. If the sampling area is not present in the QGIS Layers panel, Button 2 allows the shapefile to be located and loaded directly from a local file, after which it will appear in the dropdown menu. For instances where a suitable shapefile is not available, the plugin includes tools designed to assist in creating one, ensuring compatibility with the sampling workflow.
7.1.2 Shapefiles for Exclusion Areas
Button 3 is used to load shapefiles that define exclusion zones, areas where sampling will not be performed. This feature is optional, and exclusion zones can be left unspecified if not required. Once loaded through Button 3, the exclusion zones are displayed in a list located in the panel designated as number 4. Items in the list can be removed by double-clicking on them, allowing for easy adjustments to the sampling area.
7.1.3 Automated Sample Labeling
The text box designated as number 5 is used to define the prefix for sample labels. The plugin will then assign a consecutive numbering starting from 1 up to the total number of samples, using the entered prefix as the base for the labels. Pressing Button 6 saves the specified label prefix, confirmed by a pop-up notification indicating successful saving. If the text box number 5 is left blank, the samples will simply be numbered consecutively from 1 to the total number of samples.
7.1.4 Customizing Sample Symbology
The dropdown menu of Button 7 allows the selection of 10 different symbology styles for the samples. Once the desired style is selected, pressing Button 8 saves the selection, confirmed by a pop-up notification indicating successful saving. If no symbology is selected, the samples will default to a circular symbol with a randomly assigned fill color.
7.1.5 Setting Up Custom Symbology in QGIS
Button 9 provides optional access to the folder containing all SVG files used for the sampling point symbology. These SVG files have been exclusively designed for this plugin and are not included in QGIS by default. Installing these files in the QGIS SVG directory is not required to use them within the Sampling Time plugin; however, installation enables their use across other QGIS projects.
Installing SVG Files in QGIS:
- Open the folder: Click Button 9 to access the folder and copy its path.
- Access settings: Navigate to Settings > Options, then select the System section and locate SVG Paths.
- Add the path: Select Add a New Path, paste the copied folder path into the directory field, and press Enter.
- Confirm the selection: Click Select Folder and then OK to save the changes.
Applying SVG Files in QGIS:
After installation, the SVG files can be applied to any point vector layer in the QGIS Layers panel:
- Access the layer properties by right-clicking on the layer and selecting Properties > Symbology.
- Under the symbol settings, choose Simple Marker.
- In the Symbol Layer Type, select SVG Marker and scroll to the SVG Browser section.
- Browse the available folders, locate the folder containing the custom symbols, and select the desired SVG from the SVG Images panel.
7.1.6 About ST (Sampling Time) Button
Button 10 provides detailed information about the Sampling Time plugin, including its general description, version history, creation date, author details, and contact information. Additionally, it offers a link to the user guide as well as details about the license and usage rights.
7.2 Reset/Close Panel
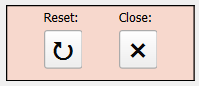
7.2.1 Reset Button
The Reset button restores the plugin to its initial state, clearing all data from the interface. When new data is added to the QGIS Layers panel, it does not automatically appear in the Sampling Time interface; a reset is necessary to update the data. Additionally, resetting the plugin can help address potential instability caused by actions performed outside its intended functionality.
7.2.2 Close Button
The plugin can be closed in two ways: by using the Close button on the interface or the “X” button in the top-right corner of the window (default on Windows systems). Using the Close button ensures a complete shutdown by performing a full reset of the interface before closing. This guarantees that when the plugin is reopened, the interface will start fresh with no residual data. In contrast, closing the plugin via the “X” button retains the data currently displayed in the interface, allowing the previous session’s data to remain available upon reopening.
7.3 Sampling Methods Panel
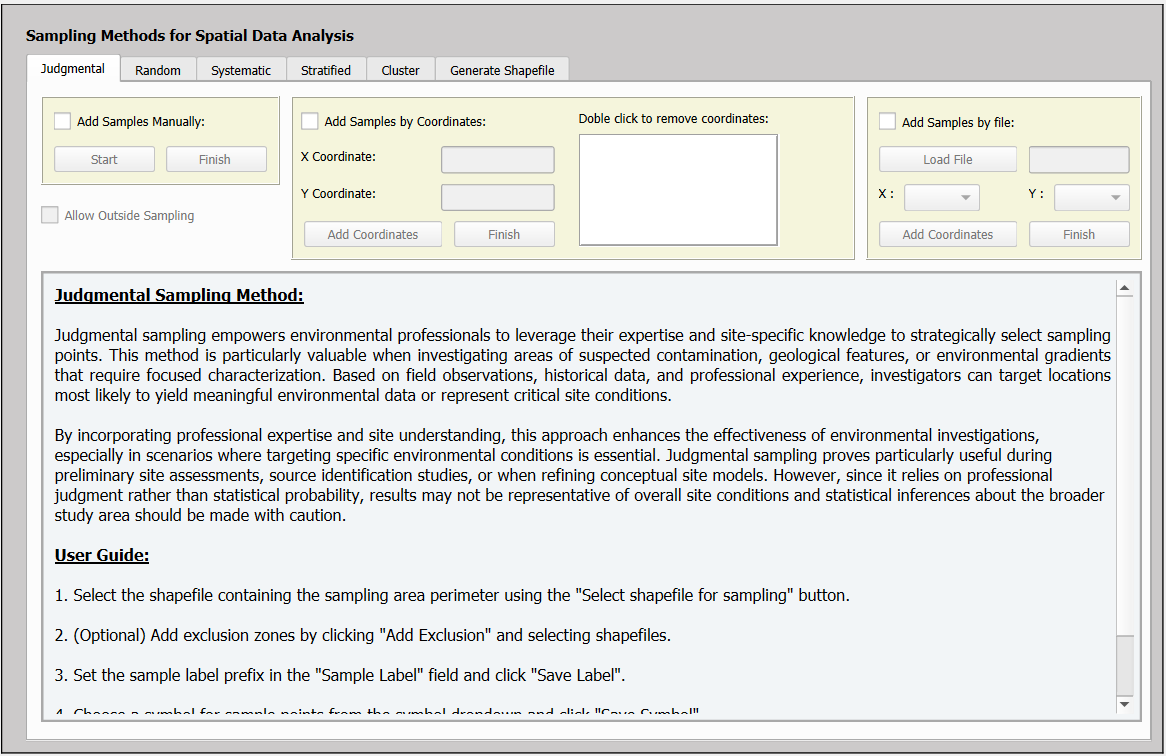
This panel hosts all available sampling methods, judgmental, random, systematic, stratified, and cluster, organized into distinct tabs. Each method functions independently, and only one method can be selected at a time. The tabs are dedicated to their respective methods, providing a conceptual description of the method and a step-by-step guide for implementation. Detailed functionality and button descriptions for each method are addressed in their corresponding sections.
The panel also includes a Generate Shapefiles tab, designed to simplify the creation of shapefiles for sampling areas, exclusion zones, strata, and clusters. The process is intuitive and guided, enabling quick and straightforward generation of basic shapefiles. For more advanced or complex shapefile creation, it is recommended to utilize QGIS’s built-in tools for greater flexibility and precision. A dedicated usage guide accompanies this section to support the shapefile generation process.
8. Plugin Functionalities Overview 📖
8.1 Generate Shapefiles
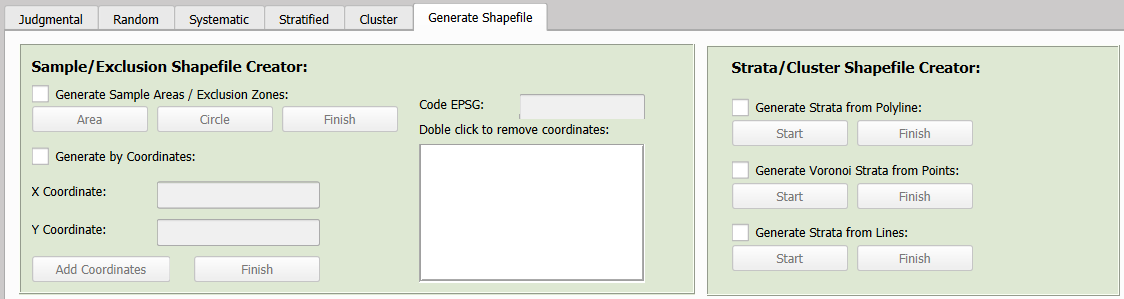
As outlined earlier, conducting any type of sampling with the Sampling Time plugin requires a shapefile defining the sampling area. This shapefile can consist of a single feature (representing a single area) for judgmental, random, or systematic sampling, or multiple features (representing a sampling area divided into distinct sections) for stratified or cluster sampling. The Generate Shapefiles tab provides a convenient solution for creating these files when they are not already available.
The Generate Shapefiles tab is divided into two main sections: one dedicated to creating sampling areas and exclusion zones, and another designed for generating strata or clusters.
8.1.1 Sampling Areas and Exclusion Zones
A) Generate Samples Areas / Exclusion Zones
This option allows the creation of shapefiles for sampling areas or exclusion zones. Polygon shapefiles can be drawn using the Area button, while circular shapefiles can be generated with the Circle button. Both shapes can be created in the same session by alternating between the two buttons. To draw on the QGIS map canvas, left-click to place points, and right-click to complete the shape. After finalizing the drawing, enter an ID in the pop-up window, click OK, specify the EPSG code for the coordinate reference system (CRS), and click Finish. The final step is to choose a folder and file name to save the shapefile.
B) Generate by Coordinates
This option allows shapefiles to be created by manually entering coordinates. Select the Generate by Coordinates checkbox and input the x and y coordinates for each point, clicking Add Coordinates after each entry. The coordinates will be listed in the interface and displayed on the QGIS map canvas in real time, connected by line segments as they are added. To remove a point, double-click it in the list. After entering the final point, specify the EPSG code for the CRS and click Finish. The polygon will close automatically, and the shapefile can then be saved by selecting a folder and providing a file name.
Important Note
When creating shapefiles by coordinates, it is essential to input points in the correct order to ensure the area is accurately defined.
8.1.2 Strata and cluster Sampling Areas
Strata and clusters can be created using three different mechanisms, all of which require a shapefile of the sampling area to be loaded in the Initiation Panel, specifically in Point 1, labeled Select Shapefile for Sampling.
A) Generate Strata from Polyline
This option allows strata or clusters to be created using polyline segments. Before starting, ensure that the shapefile containing the sampling area is loaded in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section. Once loaded, select the checkbox Generate Strata from Polyline and click Start to begin the process. Use the left mouse button to place nodes along the desired segments directly on the QGIS map canvas. Holding down Ctrl enables the creation of perfectly vertical or horizontal segments. To complete a segment, double-click the left mouse button.
Segments can be removed using the right mouse button; however, they are deleted in reverse order of creation, meaning the most recently added segment will be the first to be removed. Strata or clusters within the sampling area are generated at the intersections between the sampling area and the drawn segments. For optimal results, ensure that all polyline segments fully intersect with the sampling area and/or with other segments.
To complete the process, click Finish, select a folder to save the file, and assign a name.
B) Generate Voronoi Strata from Points
This option allows the creation of strata or clusters using Voronoi polygons, which automatically divide the sampling area based on the placement of input points. Before starting, ensure that the shapefile containing the sampling area is loaded in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section. Once loaded, select the checkbox Generate Voronoi Strata from Points and click Start to initiate the process.
Points can be added by left-clicking on the QGIS map canvas at the desired locations, representing areas of interest. The number of points added will determine the number of strata or clusters created.
To finalize the process, click Finish, select a folder to save the shapefile, and assign a name to complete the process.
C) Generate Strata from Lines
This option allows the creation of strata or clusters using freehand-drawn lines, offering greater flexibility and adaptability for more complex shapes. Before starting, ensure that the shapefile containing the sampling area is loaded in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section. Once loaded, select the checkbox Generate Strata from Lines and click Start to initiate the process.
To draw a line, hold down the left mouse button and trace the desired shape directly on the QGIS map canvas. Release the left mouse button to finalize the line. Entire lines can be deleted using the right mouse button; however, they are deleted in reverse order of creation, meaning the most recently added line will be the first to be removed.
Strata or clusters within the sampling area are generated at the intersections between the sampling area and the drawn lines. For accurate results, ensure that all lines fully intersect with the sampling area and/or with other lines to create strata or clusters correctly.
To complete the process, click Finish, choose a folder to save the file, and assign a name.
8.2 Judgmental Sampling
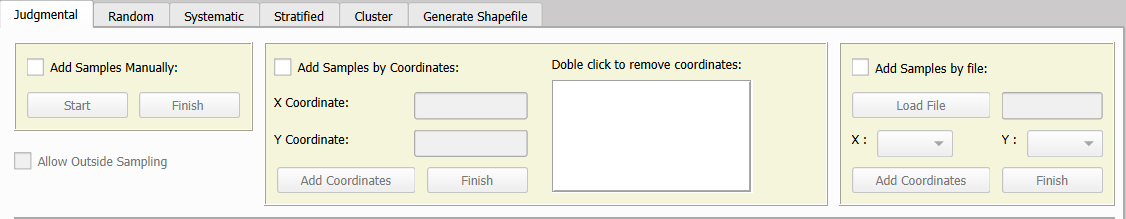
Judgmental sampling can be performed using three distinct methods: Add Samples Manually, Add Samples by Coordinates, and Add Samples by File. Before proceeding with any method, it is essential to load a shapefile of the sampling area in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section.
Several optional features are available to customize the sampling process:
- Exclusion zones: A shapefile can be loaded in the Select Exclusion Areas for Sampling section to define areas where samples should not be taken.
- Sample labeling: A custom prefix for sample labels can be entered in the Enter Sample Label Root field and saved by clicking the Save Label button.
- Sample symbology: Custom symbology can be chosen in the Select Sample Symbol section and saved using the Save Symbol button.
If no custom label is specified, samples will be automatically numbered sequentially from 1 to the total number of samples. Likewise, if no symbology is selected, a default circular symbol with a randomly assigned fill color will be applied.
A) Add Samples Manually
Selecting this option and clicking the Start button initiates the manual placement of sampling points on the QGIS map canvas. Left-click anywhere within the sampling area to add the required samples. If a sample needs to be removed, simply right-click on it.
By default, sample placement is restricted to the sampling area. To allow samples to be added outside this boundary, enable the Allow Outside Samples option before proceeding.
Once the sampling process is complete, click Finish, choose a folder, and specify a file name. The shapefile containing the samples will be generated automatically. The attribute table of the newly created shapefile will include the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Label: The sample label, derived from the specified prefix if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
B) Add Samples by Coordinates
This option allows samples to be added manually, similar to the Add Samples Manually method, but also provides the capability to place samples using their coordinates. To use this option, enter the X and Y coordinate values of the sample location and click the Add Coordinates button. If the sample falls within the sampling area, it will be automatically added to the sample list in the plugin interface and displayed on the QGIS map canvas. If the sample is located outside the sampling area or within an exclusion zone, an informational pop-up will notify the user.
To enable sample placement outside the sampling area, simply select the Allow Outside Sampling checkbox before adding the coordinates.
Samples added via coordinates can be removed by double-clicking them in the coordinate list within the plugin interface or by right-clicking directly on the sample in the map canvas.
Once all desired samples have been added, click Finish, select a folder, and provide a file name. The final shapefile containing the samples will be generated automatically. The attribute table of the resulting shapefile will include the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Label: The sample label, derived from the specified prefix if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
C) Add Samples by File
This option enables sample addition both manually and by importing a CSV or XLSX file containing sample coordinates. To get started, select this option and click the Load File button to upload the file with the sample coordinates. Once loaded, specify the columns corresponding to the X and Y coordinates within the plugin interface, then click Add Coordinates to process the data.
If the coordinates fall within the sampling area, the samples will be automatically displayed on the QGIS map canvas. If any samples are located outside the sampling area or within an exclusion zone, an informational pop-up will provide the following options:
- Add all samples,
- Add only valid samples (those that comply with the sampling criteria), or
- Cancel and select a different file.
To allow the addition of samples outside the sampling area, enable the Allow Outside Samples checkbox before importing the file.
In addition to importing samples from a file, new samples can be manually added by left-clicking on the map canvas. Any sample, whether manually added or imported, can be removed by right-clicking on it.
Once all samples have been added, click Finish, choose a folder, and specify a file name. The final shapefile will be automatically generated and loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the resulting shapefile will contain the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Label: The sample label, based on the specified prefix if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
8.3 Random Sampling
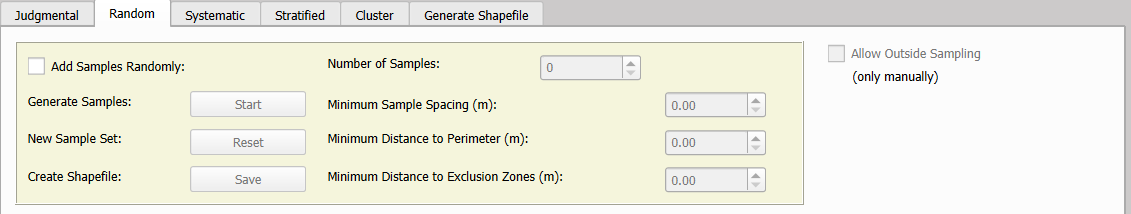
Before starting the random sampling process, it is crucial to load a shapefile containing the sampling area in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section.
To further refine the sampling process, several optional features can be utilized:
- Exclusion zones: A shapefile can be added via the Select Exclusion Areas for Sampling section to specify areas where sampling should not occur.
- Sample labeling: A custom prefix for sample labels can be defined in the Enter Sample Label Root field and saved by clicking the Save Label button.
- Sample symbology: Preferred symbology for the samples can be selected in the Select Sample Symbol section and stored using the Save Symbol button.
If no custom label is provided, the samples will be sequentially numbered from 1 to the total number of samples. Similarly, if no symbology is specified, the samples will be displayed with a default circular symbol featuring a randomly assigned fill color.
A) Add Samples Randomly
To initiate the random sampling process, it is essential to specify the desired number of samples within the sampling area. This number should be chosen carefully, as an excessively high value may lead to significant processing delays or even cause the software to crash.
To refine the sampling process, several optional parameters can be configured:
- Minimum distance between samples: Defines the required separation between individual samples (in meters), ensuring adequate spatial distribution.
- Minimum distance from the sampling area boundary: Specifies the minimum allowable distance between samples and the perimeter of the sampling area (in meters).
- Minimum distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are present, an optional buffer distance (in meters) can be set to prevent samples from being placed too close to these areas.
Once the parameters have been set, click Start to generate the sample set based on the specified criteria. If a different set of samples is required, click Reset to clear the current selection and generate a new set. In both cases, a pop-up window will confirm the total number of samples successfully placed. It is important to note that not all requested samples may be generated if the defined parameters are too restrictive.
Additional samples can be manually added by left-clicking on the QGIS map canvas, while existing samples can be removed with a right-click. To place samples outside the defined sampling area, enable the Allow Outside Samples checkbox. However, samples placed outside the area can only be added and removed manually.
To complete the sampling process, click Save, select a folder, and provide a file name. The resulting shapefile will be automatically created and loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the newly generated shapefile will include the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Label: The sample label, based on the specified prefix, if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
8.4 Systematic Sampling
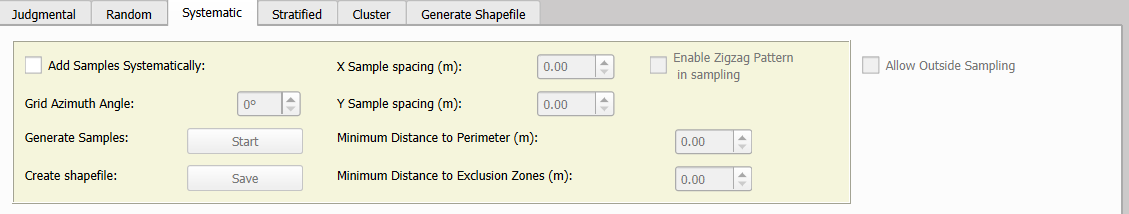
Before initiating the systematic sampling process, it is essential to load a shapefile that defines the sampling area in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section.
Several optional settings can be configured to customize the sampling process:
- Exclusion zones: A shapefile can be loaded through the Select Exclusion Areas for Sampling section to define areas where samples should not be placed.
- Sample labeling: A custom prefix for sample labels can be entered in the Enter Sample Label Root field and saved by clicking the Save Label button.
- Sample symbology: The desired symbology for the samples can be selected in the Select Sample Symbol section and applied using the Save Symbol button.
If no custom label is specified, the samples will be automatically numbered sequentially, starting from 1 up to the total number of samples. Likewise, if no symbology is selected, the samples will be displayed using a default circular symbol with a randomly assigned fill color.
A) Add Samples Systematically
The first step in systematic sampling is to define the spacing parameters along the X and Y directions, which determine the grid structure. Additionally, an optional rotation angle can be specified to adjust the grid orientation. This angle, measured in azimuth degrees from 0 to 180, uses north as the reference point.
To enhance flexibility in sample distribution, the Enable Zigzag Pattern in Sampling option can be activated. This feature introduces a zigzag pattern, helping to minimize potential cyclic or repetitive biases in the sampling process.
Several optional parameters can also be set to further refine the sampling layout:
- Minimum distance from the sampling area boundary: Ensures that samples are placed at a specified distance from the perimeter (measured in meters).
- Minimum distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are present, an additional buffer distance (in meters) can be defined to prevent samples from being placed too close to these restricted areas.
It is important to note that if the grid design includes a large number of points, the computation time required to generate the grid may significantly increase, potentially causing performance issues or software crashes. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to use realistic and sensible values for sample spacing to maintain optimal performance.
Once the desired parameters are configured, click Start to generate the sampling grid. The grid can be positioned within the sampling area by holding down the left mouse button and dragging it to the desired location. Press Enter to finalize and lock the grid in place.
After the grid has been placed, additional samples can be manually added by left-clicking, while unwanted samples can be removed with a right-click. If samples need to be placed outside the designated area, the Allow Outside Sampling checkbox must be enabled, allowing manual placement beyond the sampling area boundary.
To complete the process, click Save, select a folder, and specify a file name. The final shapefile will be automatically created and loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the generated shapefile will contain the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Label: The sample label, derived from the specified prefix, if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
8.5 Stratified Sampling
Differences Between Stratified and Cluster Sampling
Stratified and cluster sampling are both techniques used to divide a population into smaller, more manageable subgroups; however, they differ significantly in their approach and objectives.
In stratified sampling, the population is divided into distinct, homogeneous subgroups called strata based on specific characteristics such as land use, soil type, or administrative boundaries. Each stratum is treated as an independent unit, ensuring that samples are distributed proportionally or equally across all strata. The primary goal is to capture variability within each stratum, leading to more precise and representative results across the entire area. Stratified sampling is ideal when the population is known to have different subgroups with unique characteristics, allowing for targeted analysis of each.
In contrast, cluster sampling divides the population into heterogeneous subgroups called clusters, where each cluster is intended to represent the population as a whole. Rather than sampling across all clusters, a random selection of clusters is made, and then all or a portion of the elements within the chosen clusters are sampled. This method is often used to simplify data collection and reduce costs, as it allows for sampling in concentrated areas rather than spreading resources across the entire region. Cluster sampling is suitable when geographic or logistical constraints make it impractical to sample the entire population evenly.
In summary, stratified sampling ensures greater precision by sampling within specific subgroups, whereas cluster sampling focuses on practicality and efficiency by grouping elements together and sampling only selected clusters. The choice between these methods depends on the nature of the population, the objectives of the study, and the available resources.
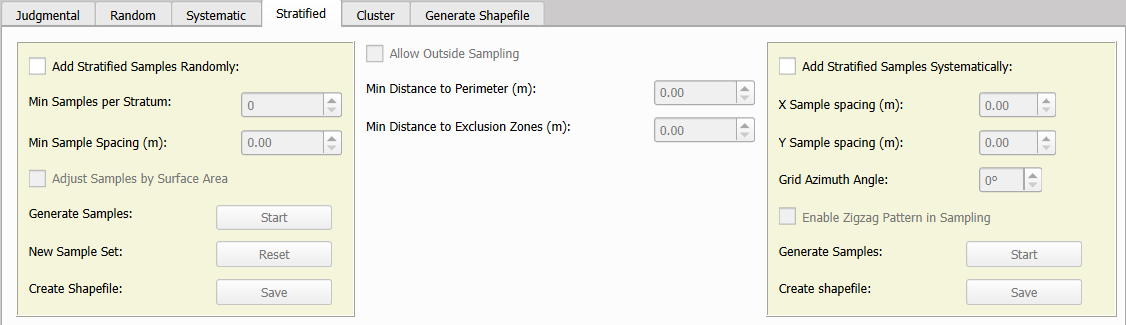
Stratified sampling can be conducted through two distinct methods: Add Stratified Samples Randomly and Add Stratified Samples Systematically. Before using either method, it is crucial to load a shapefile containing the sampling area in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section.
To further customize the sampling process, several optional features are available:
- Exclusion zones: A shapefile can be added in the Select Exclusion Areas for Sampling section to define areas where sampling should not occur.
- Sample labeling: A custom prefix for sample labels can be specified in the Enter Sample Label Root field and saved by clicking the Save Label button.
- Sample symbology: Preferred symbology for the samples can be selected in the Select Sample Symbol section and stored using the Save Symbol button.
If no label prefix is defined, the samples will be automatically numbered in sequential order, starting from 1 up to the total number of samples. Likewise, if no custom symbology is selected, the default representation will be a circular symbol with a randomly assigned fill color.
A) Add Stratified Samples Randomly
This sampling method closely resembles the Add Samples Randomly method, with the key distinction that it applies to multiple distinct areas, referred to as strata, within a larger sampling region. Each stratum is treated as an independent sampling unit.
After selecting the Add Stratified Samples Randomly option, the minimum number of samples per stratum must be defined. Sampling can be performed by assigning an equal number of samples to each stratum or by adjusting the sample distribution based on the surface area of each stratum. To enable this dynamic allocation, the Adjust Samples by Surface Area checkbox must be selected. In this case, the specified minimum sample count will be assigned to the smallest stratum, while larger strata will receive a proportionally higher number of samples.
It is essential to choose a realistic and reasonable number of samples to prevent excessive computation time or potential software crashes.
Additional optional parameters can be configured to fine-tune the sampling process:
- Spacing between samples: Defines the minimum allowable distance between samples within each stratum (in meters).
- Distance from the sampling area boundary: Ensures that samples are positioned at a defined distance from the perimeter (in meters).
- Distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are present, a buffer distance (in meters) can be set to prevent samples from being placed too close to these restricted areas.
Once all parameters are configured, click Start to generate the sample set. If a new set of samples is needed, click Reset to remove the existing samples and generate a new set. In both cases, a pop-up notification will display the total number of samples generated per stratum. It is important to note that due to restrictive parameter conditions, the specified number of samples may not always be fully allocated.
If sampling outside the defined area is necessary, the Allow Outside Sampling checkbox must be enabled. Additional samples can then be manually placed beyond the sampling boundary using a left-click, and removed with a right-click.
To complete the sampling process, click Save, select a folder, and specify a file name. A new shapefile will be generated and automatically loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the resulting shapefile will contain the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Strata: Identifies the stratum to which each sample belongs.
- Sample: Displays the label assigned to each sample.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
B) Add Stratified Samples Systematically
This sampling method expands on the systematic sampling approach by incorporating the concept of strata, which represent distinct sub-areas within a larger sampling region. Unlike standard systematic sampling that applies a uniform grid across the entire area, stratified systematic sampling allows for independent analysis of each stratum. However, a single grid is used across the entire region, ensuring consistent spacing while facilitating separate processing for each stratum.
The process begins by defining the spacing parameters along the X and Y axes, which establish the grid structure across all strata. Additionally, an optional rotation angle can be specified to adjust the grid’s orientation. This angle, measured in azimuth degrees from 0 to 180, considers north as the reference point.
To further enhance the sampling distribution, the Enable Zigzag Pattern in Sampling option can be activated. This feature introduces a zigzag arrangement, which helps to reduce potential cyclic or repetitive biases within each stratum, providing a more representative sample distribution.
Several optional parameters are available to refine the sampling process:
- Minimum distance from the sampling area boundary: Ensures that samples are positioned at a specified distance from the perimeter (in meters).
- Minimum distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are defined, a buffer distance (in meters) can be set to prevent samples from being placed too close to restricted areas.
It is essential to set realistic values for grid spacing and sample count, as an overly dense grid can significantly impact computational performance and may lead to software crashes. Choosing appropriate parameters ensures an efficient and stable sampling process.
Once all parameters are configured, clicking Start generates the sampling grid. The grid can be positioned within the sampling area by holding the left mouse button and dragging it to the desired location. Pressing Enter confirms and locks the grid in place.
Once the grid is set, additional samples can be manually added by left-clicking, while unwanted samples can be removed with a right-click. If samples need to be placed outside the sampling area, enabling the Allow Outside Sampling option permits manual placement beyond the defined boundary.
To complete the process, click Save, select a folder, and provide a file name. The generated shapefile will be automatically saved and loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the created shapefile will include the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier for each sample.
- Strata: The stratum to which each sample belongs.
- Label: The sample label, based on the specified prefix, if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
8.6 Cluster Sampling
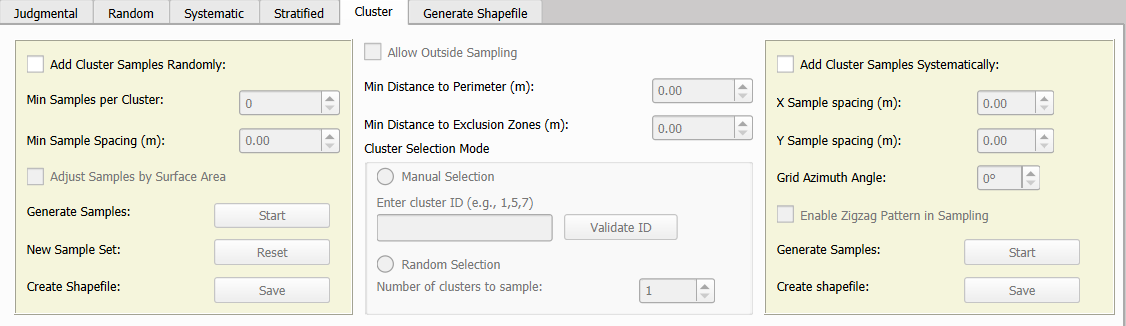
Cluster Sampling can be carried out using two distinct methods: Add Cluster Samples Randomly and Add Cluster Samples Systematically. Before initiating either method, it is essential to load a shapefile of the sampling area in the Select Shapefile for Sampling section.
To further refine and customize the sampling process, several optional settings are available:
- Exclusion zones: A shapefile can be loaded in the Select Exclusion Areas for Sampling section to specify areas where samples should not be placed.
- Sample labeling: A custom prefix for sample labels can be defined in the Enter Sample Label Root field and saved by clicking the Save Label button.
- Sample symbology: Custom symbology can be chosen in the Select Sample Symbol section and saved using the Save Symbol button.
If no label prefix is provided, the samples will be automatically numbered sequentially, starting from 1 up to the total number of samples. Similarly, if no symbology is specified, the samples will be displayed using a default circular symbol with a randomly assigned fill color.
A) Add Cluster Samples Randomly
This method applies the principles of random sampling to clusters, allowing for sample distribution across multiple predefined clusters within the larger study area.
Clusters to be sampled can be selected in two ways:
Manual Selection:
-
- Enter the IDs of the clusters to be sampled in the provided field, separated by commas.
- Click the Validate ID button to confirm the selected clusters and ensure they exist within the dataset.
- Any time the cluster selection is modified, the Validate ID button must be clicked to register the changes correctly.
Random Selection:
-
- Specify the number of clusters to be selected for sampling.
- The plugin will randomly choose the specified number of clusters from the available dataset.
Once the clusters have been selected, whether manually or randomly, the sampling process continues similarly to regular random sampling. Users must specify the minimum number of samples per cluster, ensuring that the chosen value is realistic to prevent excessive computation times or software crashes.
When configuring the sampling process, the Adjust Samples by Surface Area option can be enabled to distribute samples proportionally according to the cluster’s surface area. If this option is checked, the specified value represents the minimum number of samples assigned to the smallest cluster, with larger clusters receiving proportionally more samples. If left unchecked, all clusters will receive the same fixed number of samples regardless of their size.
Several optional parameters can be configured to refine the sampling process:
- Minimum distance between samples: Defines the required separation between samples (in meters).
- Minimum distance from the sampling area boundary: Ensures a specified buffer from the perimeter (in meters).
- Minimum distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are present, a buffer distance (in meters) can be applied to prevent samples from being placed too close to restricted areas.
Once all parameters are set, clicking the Start button will generate the sample set according to the defined criteria. If a new set is required, clicking the Reset button will clear the current samples and generate a new set. A pop-up will display the total number of samples generated per cluster. It is important to note that restrictive parameters may prevent the full placement of the requested samples.
Samples can be manually added or removed by left- and right-clicking, respectively. If sampling outside the defined area is necessary, enabling the Allow Outside Samples checkbox allows for manual placement beyond the sampling area boundary.
To complete the sampling process, click Save, select a folder, and assign a file name. A new shapefile will be generated and automatically loaded into QGIS. The attribute table of the created shapefile will contain the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Cluster: Indicates the cluster to which each sample belongs.
- Label: The sample label, based on the specified prefix if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.
B) Add Cluster Samples Systematically
This method incorporates the systematic sampling approach into cluster sampling, enabling structured sample placement within predefined clusters across the study area. A single sampling grid is applied uniformly across all clusters, ensuring consistent spacing while allowing for independent processing within each cluster.
Clusters to be sampled can be selected through two methods:
Manual Selection:
-
- Input the IDs of the clusters to be sampled, separated by commas.
- Click the Validate ID button to confirm their existence and register them for sampling.
- Whenever changes are made to the selected clusters, the Validate ID button must be clicked again to update the selection.
Random Selection:
-
- Specify the number of clusters to be sampled.
- The plugin will randomly select the specified number of clusters from the available dataset.
Once the cluster selection is finalized, the grid parameters must be defined:
- Spacing parameters: Set the spacing along the X and Y directions to determine the grid structure.
- Grid rotation angle: An optional azimuth angle (0 to 180 degrees) can be set to adjust the grid orientation, with north as the reference.
- Zigzag pattern: The Enable Zigzag Pattern in Sampling option can be selected to introduce a zigzag pattern, helping to reduce potential biases.
Additional optional parameters can also be configured:
- Minimum distance from the sampling area boundary: Ensures that samples are placed at a specified distance from the perimeter (in meters).
- Minimum distance from exclusion zones: If exclusion zones are included, a buffer distance (in meters) can be set to avoid placing samples too close to these areas.
It is important to use realistic values for grid spacing and sample count, as an excessive number of grid points may slow down processing and could lead to software crashes.
Once all parameters are configured, click Start to generate the sampling grid. The grid can be positioned within the sampling area by holding down the left mouse button and dragging it to the desired location. Press Enter to lock the grid in place.
Additional samples can be manually added or removed using left and right clicks, respectively. If sampling beyond the defined area is required, enabling the Allow Outside Samples checkbox allows for manual placement outside the sampling area.
To finalize the process, click Save, select a folder, and provide a file name. The generated shapefile will be automatically loaded into QGIS. The attribute table will contain the following columns:
- ID: A unique identifier assigned to each sample.
- Cluster: Indicates the cluster to which each sample belongs.
- Label: The sample label, based on the specified prefix if provided.
- X Coordinate: The X coordinate of the sample location.
- Y Coordinate: The Y coordinate of the sample location.